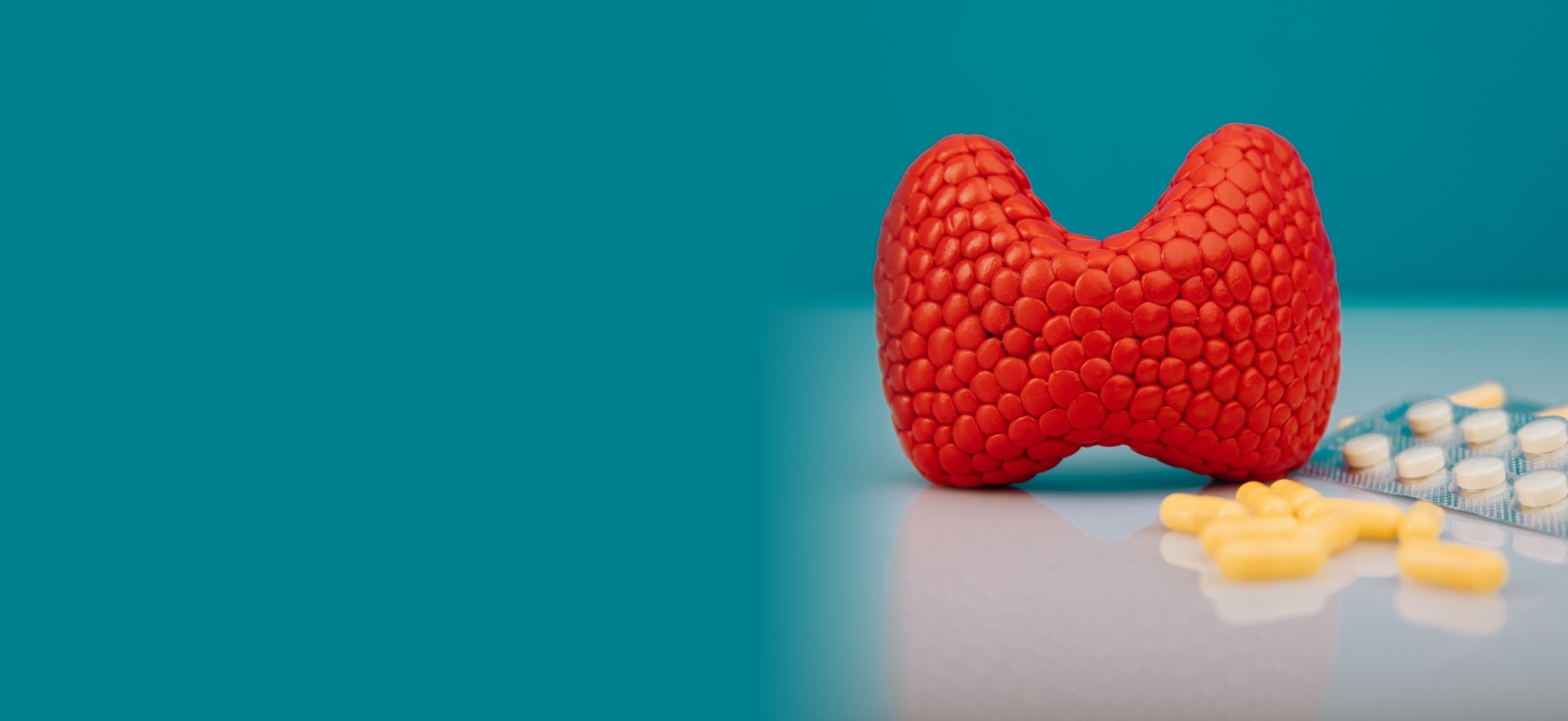
Signs & Symptoms:

- A lump or swelling in the neck, often near the Adam’s apple
- Hoarseness or a change in the voice
- Difficulty swallowing
- Persistent pain in the throat or neck
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and Unexplained weight loss
- A persistent cough that is not due to a cold
Causes
Stages:

Stage 1: The cancer is small and only in the thyroid gland.
Stage 2: The cancer has grown larger and may have spread to the lymph nodes.
Stage 3: The cancer has spread to other parts of the neck.
Stage 4: The cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs or bones.
Risk Factors
Exposure to radiation: People who have been exposed to radiation, such as those who received radiation therapy to the head or neck as children, have a higher risk of developing thyroid cancer.
Genetic mutations: Some people may have inherited mutations in genes that increase the risk of thyroid cancer.
Family history: People with a family history of thyroid cancer are more likely to develop the disease.
Age: Thyroid cancer is more common in people over the age of 60.
Prevention, Screening & Diagnosis:
Reduce radiation exposure: protect yourself from unnecessary radiation exposure.
Understand your family history: Be aware of any history of thyroid cancer in your family.
Regular check-ups: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider can help detect thyroid cancer early.
Thyroid function tests: Thyroid function tests can detect abnormalities in the thyroid gland and help diagnose thyroid cancer.
Imaging tests: Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT and MRI scan, can help detect a lump or mass in the thyroid gland.
Treatment options:
Surgery: Surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid gland is the most common treatment for thyroid cancer.
Radiation therapy: Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells.
Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells.
Targeted therapy: Targeted therapy uses drugs that target specific mutations or proteins in cancer cells
Hormone therapy: Hormone therapy is used to block the production of hormones that can fuel the growth of cancer cells
Post-treatment follow-up:
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider
Thyroid function tests to monitor hormone levels
Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, to check for any signs of recurrent cancer
Medications to replace the hormones the thyroid gland would normally produce, if surgery has removed the entire gland.
It’s important to note that early detection and treatment are key for successful outcome for Thyroid cancer and regular check-ups are important, it’s also important to consult with an expert doctor/surgeon for a personalized treatment plan, that best suits your case.
Contact Us
Visiting Hours
OPEN 24 hours 7 days a week.
OPD Timings : Monday to Saturday
( 9:00 AM to 5:30 PM )
Appointments
Emergency
Visit the hospital
MGM Cancer Institute
No 119 & 121, Nelson Manickam Road, Raajeswari Street, Rajaram Mehta Nagar,
Aminjikarai, Chennai – 600029